7 Control
Parameters in this section allow the control loop to be set up for optimum control conditions. An example of a temperature control loop is shown below:-
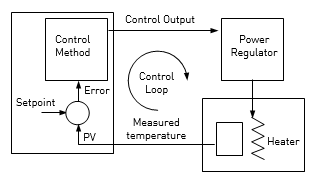
The actual temperature measured at the process (PV) is connected to the input of the controller. This is compared with a setpoint (or required) temperature (SP). If there is an error between the set and measured temperature the controller calculates an output value to call for heating or cooling. The calculation depends on the process being controlled but normally uses a PID algorithm. The output(s) from the controller are connected to devices on the plant which cause the heating (or cooling) demand to be adjusted which in turn is detected by the temperature sensor. This is referred to as the control loop or closed loop control.