- Phone:513.772.0060
- Address:7205 Edington Dr. Cincinnati, OH 45249
SSi’s Load Entry 3 software is part of the SSi SuperDATA suite of programs. Load Entry assists with recipe management and tracking by providing a single, PC-based interface to control all activities for a heat treat facility. Load Entry is accessible from any computer setup as a SuperDATA workstation, allowing multiple access terminals throughout a facility.
| Seamlessly integrates with existing SSi and some third party controllers for creating, starting, and stopping recipes. |
| Works with SSi Configurator program to import recipes that have already been created. |
| Allows person to enter various operations, furnaces, recipes, parts and users. |
| Enables you to “apply” these items to one another as required by your facility. |
| Allows for easy tracking, management, and information retrieval. |
| Saves time and money. |
| Scanning capabilities. |
Requires SuperDATAPro with DataCenter. |
Minimum PC Specifications. |
SuperDATA Server / Workstation. |
Dell Precision T5820 Tower. |
Windows 10 Professional, 64-bit. |
Intel Xeon W-2223 Four Core Processor. |
| 32GB RAM Memory. |
– Two (2) 512GB Solid State Hard Drives |
– Configured for RAID 1 |
– Keyboard and Mouse |
– 3 Year Basic Hardware Service Provided by Dell |
Monitor Sold Separately (PN 31372) |
| Define the user their password and the claims to operational variables in the system. |
| Define the operations in your heat treating facility. |
| Define the assets in use at your facility. |
| Create recipes, sequence of movement for specific parts through assets, parts with references to operations/recipes/sequences, work order template, custom fields for work orders. |
What is Planned Maintenance?
Planned maintenance refers to a proactive approach to equipment management, where maintenance activities are scheduled and carried out based on predetermined plans rather than in response to unexpected breakdowns. The goal of planned maintenance is to optimize equipment performance, extend its lifespan, and reduce the likelihood of unplanned downtime. It involves activities such as routine inspections, preventive maintenance, and predictive maintenance, which help identify potential issues before they result in failures. By focusing on regular upkeep, planned maintenance enhances equipment reliability, minimizes costs associated with reactive repairs, and improves overall operational efficiency.
Key tasks for Planned Maintenance:
Benefits of Planned Maintenance:
How to Implement Planned Maintenance:
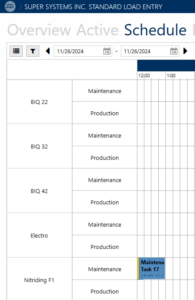
Planned Maintenance with LE3
The SSI Load Entry system is a module of our SuperDATA SCADA package that provides the next level of visibility, management and traceability for heat treat processes. The load entry provides a customizable overview of assets, a recipe database, a parts database, integration with all SuperDATA tools, load tracking, efficiency reporting in the areas of utilization and gap reasons between loads, and much more. As with anything SSi develops and manufactures, we are looking to provide the best integrated tools yielding operational efficiencies in heat treating and the areas of scheduling and maintenance are just that.
Implementing planned maintenance with LE3 involves creating a structured approach to managing equipment and maintenance based on usage or load data. With the help of LE3’s effortless tracking, management, and information retrieval you can collect accurate load data logs that track the operational hours and load conditions of machinery or systems.
Maintenance schedules can be created to align with predefined usage thresholds and industry specifications (AMS 2750, CQI-9, etc), ensuring equipment is serviced before any potential failure or non-compliance.
With Load Entry 3 “Maintenance” and “Scheduling”, maintenance and furnace activities can be planned to minimize the impact on production and maximize equipment utilization to avoid costly unplanned downtime. Regular analysis from LE3 helps optimize the maintenance intervals, ensuring that machinery runs efficiently. By aligning maintenance efforts with load-based data, companies can proactively extend the lifespan of equipment, improve reliability, reduce unplanned downtime, and cut down on costs.
Planned activities to address industry specifications ensure compliance of equipment. The integration between LE3 and maintenance will prevent equipment for being used to run parts where equipment compliance has expired.